
Graph Benchmarks V1
Founders HelixDB
These benchmarks have since been amended to give our competitors a more level playing field. To view those benchmarks go to: https://www.helix-db.com/blog/graph-benchmarks-v1-1
At HelixDB we've been focused on performance for the last few weeks. Here are our benchmarks for HelixDB, Neo4j, and Postgres (edges as joins) on a realistic graph dataset.
We're still working on Vector benchmarks - stay tuned!
TL;DR
(10,000 users, 500,000 items, ~4M edges).
HelixDB crushes graph workloads (5–20x faster) and is your best bet for production graph workloads (GraphRAG, recommendations, social graphs)
Neo4j 5-20x slower than HelixDB
Postgres is 10–80x slower
Dataset hash
ffed7c34a46dc90e· Conducted November 2025 · https://github.com/helixdb/graph-vector-bench
How to Read This
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| P50 / P95 / P99 | 50th / 95th / 99th percentile latency |
| ops/sec | Successful operations per second (throughput) |
| FixedConcurrency | Sustained load at N concurrent clients |
| FixedQPS | Constant request rate, measures latency stability |
Test Environment
Hardware: AWS c6g.2xlarge (eu-west-2) · 8 vCPUs (ARM Neoverse-N1) · 16 GB RAM · 500 GB gp3 EBS=
Software: Ubuntu 24.04 LTS · HelixDB v2.1.0 · Neo4j 2025.09.0 (G1GC) · PostgreSQL 16.10
Benchmark: 2s warmup · 5s measurement window · FixedConcurrency (100/200/400/800) + FixedQPS (400/800/1600)
Dataset: 10k users across 25 countries · 500k items across 1k categories · ~4M edges (~400/user)
Workloads Tested
| ID | Name | Description | Example Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PointGet | Retrieve entity by ID | Product detail fetch |
| 2 | OneHop | Traverse all user -> item edges | Watch history |
| 3 | OneHopFilter | Traverse + filter by category | "Action movies watched" |
Results Summary
| Workload | Raw Winner | Performance Gap |
|---|---|---|
| PointGet | HelixDB | 12x Postgres, 16x Neo4j |
| OneHop | HelixDB | 5.9x Neo4j, 13x Postgres |
| OneHopFilter | HelixDB | 4.2x Neo4j, 20x Postgres |
Detailed Results
1 · PointGet — Simple ID Lookup
Retrieve single item by ID (product detail, user profile).
Winner: HelixDB — 12x Postgres, 16x Neo4j
FixedConcurrency Results
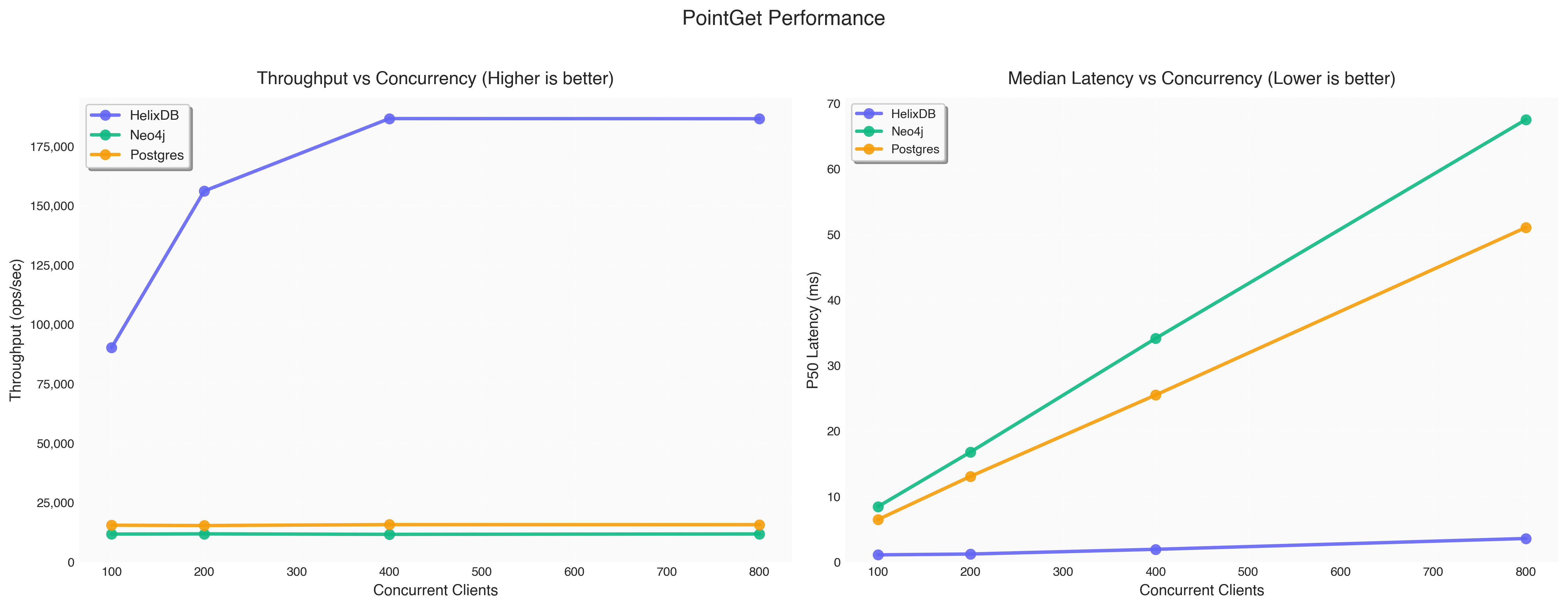
| Database | Concurrency | Throughput (ops/sec) | P50 Latency (ms) | P95 Latency (ms) | P99 Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HelixDB | 100 | 90,238.4 | 1.07 | 1.29 | 1.41 |
| Neo4j | 100 | 11,706.0 | 8.43 | 9.11 | 11.30 |
| Postgres | 100 | 15,435.0 | 6.46 | 6.61 | 6.71 |
| HelixDB | 200 | 156,136.0 | 1.20 | 1.62 | 1.94 |
| Neo4j | 200 | 11,802.0 | 16.77 | 18.72 | 19.78 |
| Postgres | 200 | 15,307.4 | 13.05 | 13.34 | 13.47 |
| HelixDB | 400 | 186,642.4 | 1.92 | 2.81 | 3.44 |
| Neo4j | 400 | 11,592.2 | 34.12 | 37.61 | 38.86 |
| Postgres | 400 | 15,685.6 | 25.47 | 25.86 | 26.16 |
| HelixDB | 800 | 186,590.8 | 3.57 | 6.73 | 8.62 |
| Neo4j | 800 | 11,771.8 | 67.52 | 70.90 | 71.72 |
| Postgres | 800 | 15,670.2 | 51.05 | 51.95 | 52.94 |
FixedQPS Results
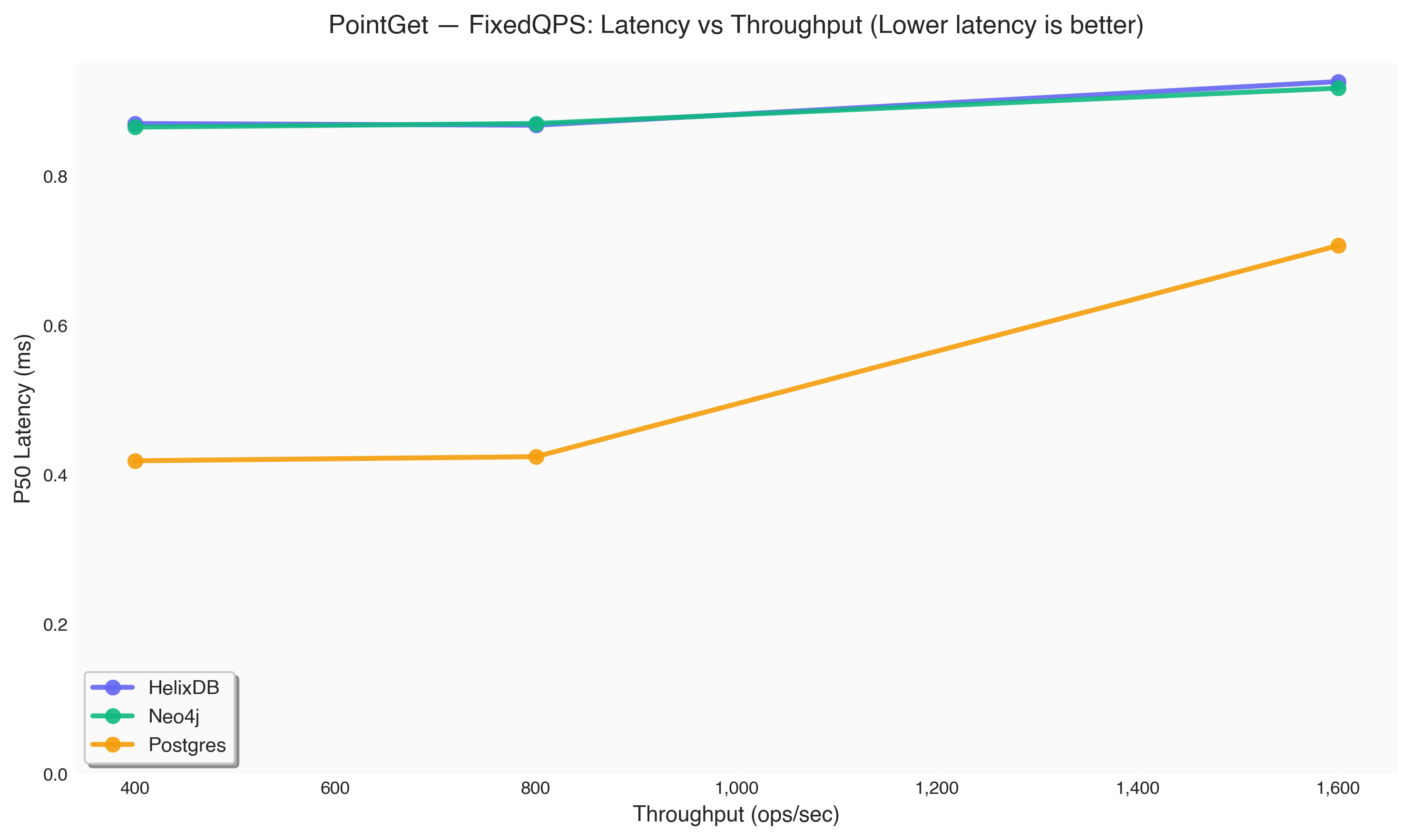
| Database | Target QPS | Actual Throughput (ops/sec) | P50 Latency (ms) | P95 Latency (ms) | P99 Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HelixDB | 400 | 400.2 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.97 |
| Neo4j | 400 | 400.2 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.93 |
| Postgres | 400 | 400.2 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.46 |
| HelixDB | 800 | 800.2 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.96 |
| Neo4j | 800 | 800.2 | 0.87 | 0.94 | 0.97 |
| Postgres | 800 | 800.0 | 0.42 | 0.50 | 0.53 |
| HelixDB | 1600 | 1,600.0 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 1.10 |
| Neo4j | 1600 | 1,600.0 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 1.03 |
| Postgres | 1600 | 1,600.0 | 0.71 | 1.33 | 1.36 |
2 · OneHop — Graph Traversal
Fetch all items a user interacted with (~400 edges/user).
Winner: HelixDB — 5.9x Neo4j, 13x Postgres
FixedConcurrency Results
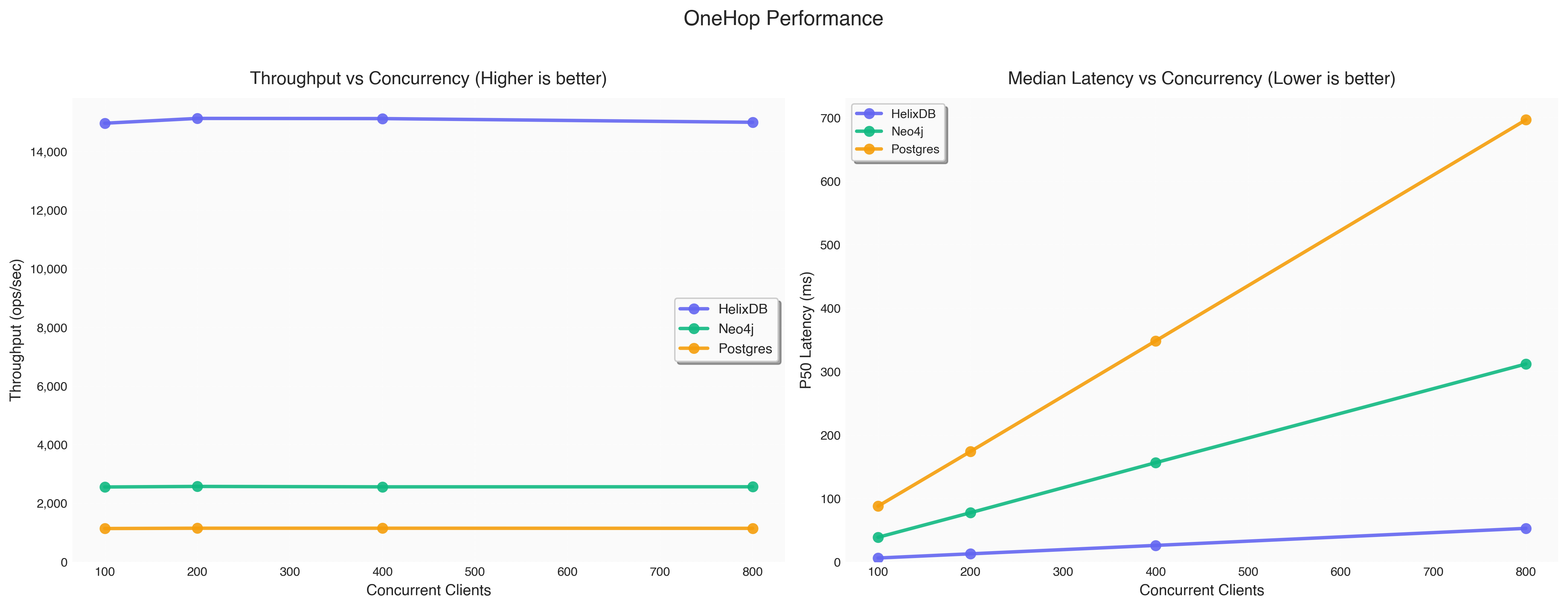
| Database | Concurrency | Throughput (ops/sec) | P50 Latency (ms) | P95 Latency (ms) | P99 Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HelixDB | 100 | 14,964.6 | 6.09 | 11.87 | 15.30 |
| Neo4j | 100 | 2,555.0 | 38.75 | 42.96 | 46.08 |
| Postgres | 100 | 1,138.2 | 87.84 | 89.38 | 90.38 |
| HelixDB | 200 | 15,129.2 | 12.72 | 18.74 | 22.21 |
| Neo4j | 200 | 2,574.0 | 77.53 | 81.04 | 82.36 |
| Postgres | 200 | 1,148.4 | 174.13 | 176.07 | 177.03 |
| HelixDB | 400 | 15,122.8 | 25.96 | 32.00 | 35.50 |
| Neo4j | 400 | 2,560.0 | 156.40 | 160.08 | 161.52 |
| Postgres | 400 | 1,148.4 | 348.39 | 350.02 | 351.22 |
| HelixDB | 800 | 14,996.8 | 52.84 | 58.88 | 62.44 |
| Neo4j | 800 | 2,562.2 | 311.93 | 317.19 | 318.83 |
| Postgres | 800 | 1,144.6 | 696.85 | 698.79 | 699.19 |
FixedQPS Results
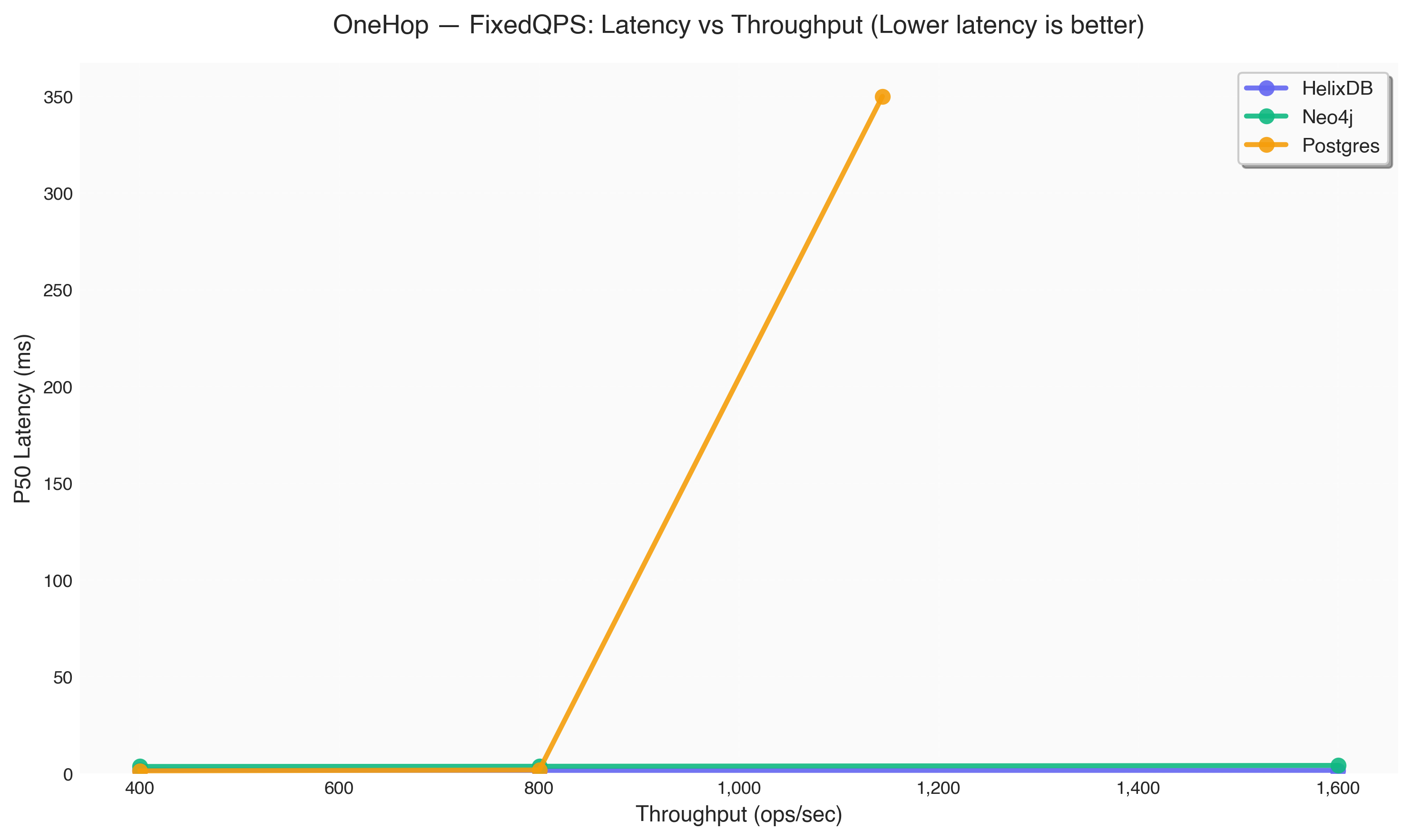
| Database | Target QPS | Actual Throughput (ops/sec) | P50 Latency (ms) | P95 Latency (ms) | P99 Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HelixDB | 400 | 400.2 | 1.70 | 2.51 | 2.65 |
| Neo4j | 400 | 400.2 | 3.52 | 3.97 | 4.09 |
| Postgres | 400 | 400.2 | 1.27 | 1.37 | 1.44 |
| HelixDB | 800 | 800.2 | 1.51 | 2.45 | 2.67 |
| Neo4j | 800 | 800.2 | 3.62 | 4.19 | 4.72 |
| Postgres | 800 | 800.2 | 1.70 | 2.70 | 2.84 |
| HelixDB | 1600 | 1,600.0 | 1.53 | 2.43 | 2.73 |
| Neo4j | 1600 | 1,600.2 | 4.06 | 5.09 | 5.90 |
| Postgres | 1600 | 1,143.8 | 349.81 | 351.85 | 352.76 |
3 · OneHopFilter — Filtered Traversal
Find items a user interacted with in a specific category.
Winner: HelixDB — 4.2x Neo4j, 20x Postgres
FixedConcurrency Results
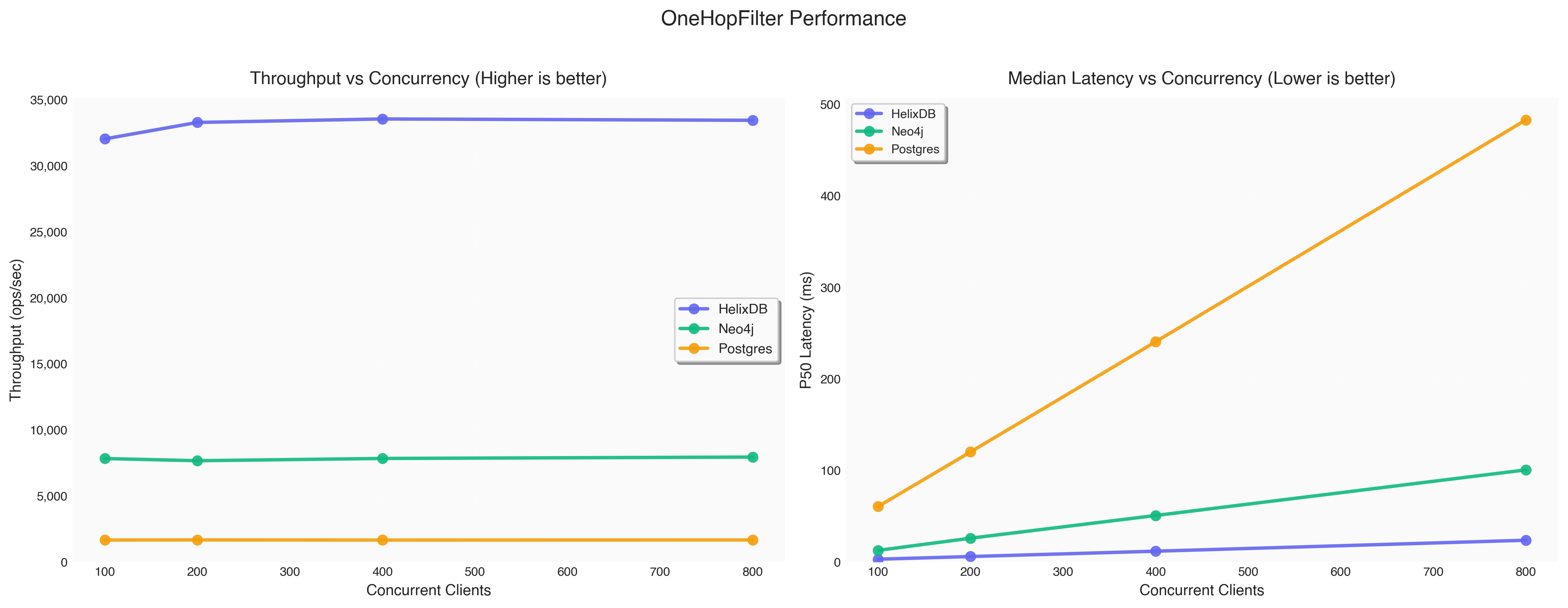
| Database | Concurrency | Throughput (ops/sec) | P50 Latency (ms) | P95 Latency (ms) | P99 Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HelixDB | 100 | 32,030.2 | 2.94 | 5.19 | 7.54 |
| Neo4j | 100 | 7,826.0 | 12.56 | 14.80 | 16.85 |
| Postgres | 100 | 1,654.4 | 60.44 | 61.32 | 61.61 |
| HelixDB | 200 | 33,277.0 | 5.84 | 8.96 | 12.93 |
| Neo4j | 200 | 7,660.2 | 25.87 | 28.49 | 29.41 |
| Postgres | 200 | 1,663.6 | 120.12 | 121.57 | 122.07 |
| HelixDB | 400 | 33,540.8 | 11.67 | 16.31 | 19.85 |
| Neo4j | 400 | 7,832.0 | 50.68 | 53.65 | 54.84 |
| Postgres | 400 | 1,653.0 | 240.47 | 254.54 | 256.58 |
| HelixDB | 800 | 33,438.6 | 23.64 | 28.32 | 32.03 |
| Neo4j | 800 | 7,935.8 | 100.48 | 104.09 | 105.07 |
| Postgres | 800 | 1,659.8 | 482.84 | 485.47 | 486.47 |
FixedQPS Results
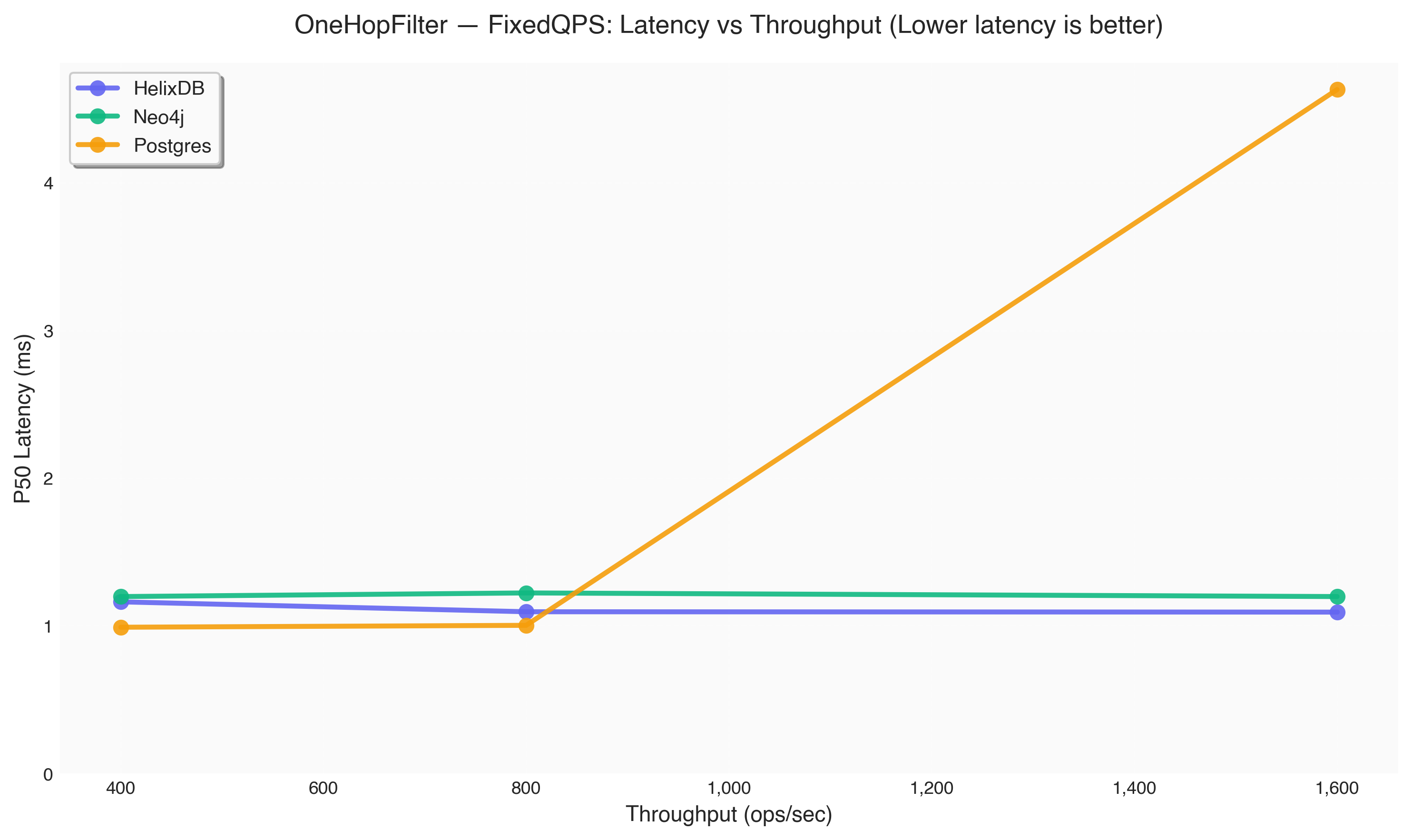
| Database | Target QPS | Actual Throughput (ops/sec) | P50 Latency (ms) | P95 Latency (ms) | P99 Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HelixDB | 400 | 400.2 | 1.16 | 1.21 | 1.23 |
| Neo4j | 400 | 400.2 | 1.20 | 1.25 | 1.31 |
| Postgres | 400 | 400.2 | 0.99 | 1.13 | 1.31 |
| HelixDB | 800 | 800.2 | 1.09 | 1.15 | 1.19 |
| Neo4j | 800 | 800.0 | 1.22 | 1.28 | 1.32 |
| Postgres | 800 | 800.0 | 1.00 | 1.62 | 1.67 |
| HelixDB | 1600 | 1,600.2 | 1.09 | 1.28 | 1.38 |
| Neo4j | 1600 | 1,600.0 | 1.20 | 1.35 | 1.68 |
| Postgres | 1600 | 1,600.0 | 4.63 | 6.50 | 7.40 |
Performance Highlights
| Database | Best At | Latency (P50) |
|---|---|---|
| HelixDB | Graph operations | 0.9–2.5 ms |
| Neo4j | Graph operations | 2.0–2.1 ms |
| Postgres | SQL | 5–40 ms |
Limitations & Reproducibility
What we didn't test:
- Cold-start latency
- Insertion times
- Memory footprint during ingestion
- Operational complexity
How to reproduce:
- Dataset hash: ffed7c34a46dc90e
- Raw JSON results, configs, and benchmark driver in repo
- Tests: November 2025, AWS c6g.2xlarge (eu-west-2)
The Bottom Line
For graph workloads (GraphRAG, Agentic systems, recommendations, social graphs):
-> Use HelixDB. The 5–20x graph advantage dominates in real-world scenarios where traversals are frequent.
Benchmark data + scripts: https://github.com/helixdb/graph-vector-bench